Test Mission Template
The "Test Mission" template in Litmus provides a framework for evaluating your AI model's performance in multi-turn interactions, simulating a more realistic conversational flow or task-oriented dialogue. Unlike "Test Runs," which treat test cases as isolated units, "Test Missions" use the AI's responses from previous turns to guide subsequent interactions.
Structure
A "Test Mission" template is structured similarly to a "Test Run" template but with key differences:
- Template ID: A unique identifier for your template.
- Mission Data: An array of missions, each containing:
- Mission: A description of the overall task or goal the AI should achieve through the conversation.
- Mission Result: The expected outcome or state at the end of a successful mission. This is used as a golden response to evaluate the entire conversation using an LLM.
- Filter (optional): Comma-separated keywords or categories to organize and filter missions.
- Source (optional): A source identifier for the mission.
- Block (optional): A boolean (true/false) indicating whether this mission should be excluded from the run.
- Category (optional): A category or label for the mission.
- Mission Duration: An integer specifying the maximum number of interaction turns allowed for each mission.
- Request Payload: A JSON object defining the structure of the API request sent to the AI model, including a placeholder
{query}for the AI's generated input. - Pre-Request and Post-Request (optional): JSON objects defining optional requests to be executed before and after each turn in the mission, respectively.
- LLM Evaluation Prompt (optional): A prompt guiding the LLM in evaluating the overall success of the mission based on the conversation history and the expected
Mission Result. This prompt is used in theevaluate_missionfunction.
Purpose
"Test Mission" templates aim to:
- Assess conversational fluency and coherence: Evaluate how well your AI maintains a natural and meaningful dialogue flow.
- Test goal-oriented behavior: Verify if your AI can achieve predefined tasks or goals through its interactions.
- Identify limitations in context understanding: Detect scenarios where your AI struggles to maintain context or follow instructions across multiple turns.
- Evaluate task completion and outcome: Assess the success of the mission based on the final state of the conversation and its alignment with the expected
Mission Result.
Scenarios
Good Use Cases
- Evaluating chatbot or dialogue system performance: Assess how naturally and effectively your AI interacts in a conversational setting.
- Testing task-oriented agents: Verify if your AI can successfully complete tasks like booking appointments, ordering food, or providing customer support.
- Evaluating multi-step reasoning and problem-solving abilities: Assess your AI's capacity to break down complex goals into manageable steps and execute them through its interactions.
Bad Use Cases
- Single-turn interactions or simple question answering: "Test Missions" are overkill for scenarios where each input is independent. Use "Test Runs" for these simpler cases.
- Testing functionalities that don't involve conversational flow: Avoid using "Test Missions" for tasks like sentiment analysis or text classification, which don't require multi-turn interactions.
Starting a Test Mission
CLI
- Get your
RUN_IDandTEMPLATE_ID. - Run the following
litmusCLI command:bashlitmus start $TEMPLATE_ID $RUN_ID
API (Simple)
- Construct a JSON payload:json
{ "run_id": "your-unique-run-id", "template_id": "your-template-id" } - Send a POST request to the
/runs/submit_simpleendpoint.
API (Advanced)
- Construct a JSON payload:json
{ "run_id": "your-unique-run-id", "template_id": "your-template-id", "pre_request": { ... }, // Optional "post_request": { ... }, // Optional "test_request": { ... }, "template_type": "Test Mission", "mission_duration": <number_of_turns> // Required for Test Missions } - Send a POST request to the
/runs/submitendpoint.
UI
- Navigate to the "Start New Run" page.
- Select your "Test Mission" template.
- Enter your
RUN_ID. - The UI should display input fields for
Mission Durationand allow you to define or edit missions. - Submit the run.
Configuration
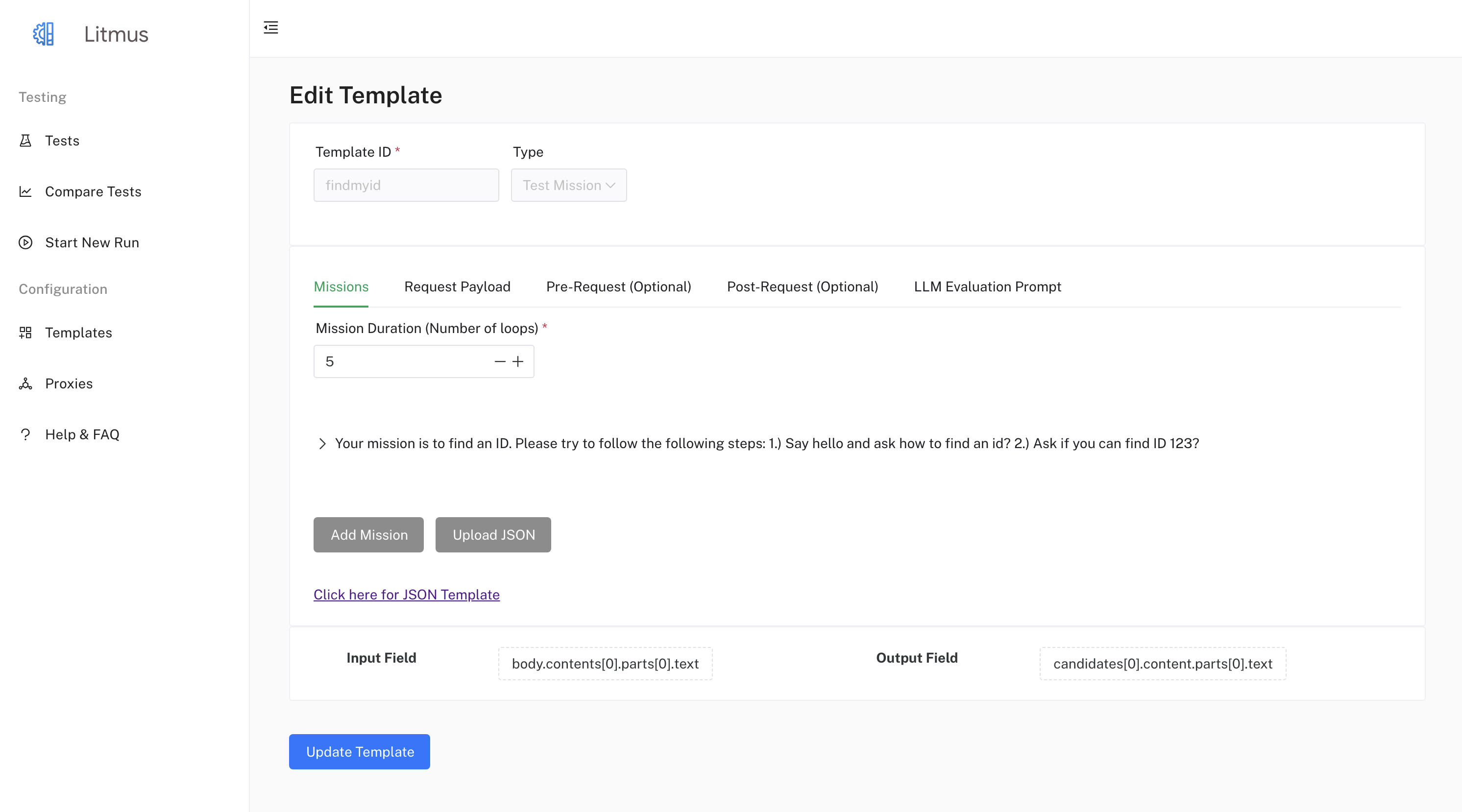
You can configure various aspects of a "Test Mission" template in the UI, including:
- Modifying the Mission Data: In the Mission tab, you can define or update missions by adding or removing mission items. Each mission item requires a mission description and an expected mission result. You can optionally provide additional data like filter, source, block, and category for each mission item.
- Modifying the Request Payload: In the Request Payload tab, modify the
Request Payloadto match your API requirements by using the built-in JSON editor. Use placeholders (e.g.,{query}) for dynamic values from your test cases or missions. For "Test Missions", the {query} placeholder will be dynamically replaced with the LLM's generated requests in each turn. - Defining or updating the Pre-Request and Post-Request: Navigate to the Pre-Request and Post-Request tabs and use the built-in JSON editor to define or update the pre-request and post-request payloads.
- Crafting the LLM Evaluation Prompt: In the LLM Evaluation Prompt tab, enter your prompt in the text area.
- Selecting the appropriate Input Field and Output Field:
- Click on the "Input Field" button. A drawer will open displaying the "Request Payload" as a JSON Tree. Click on the node representing the field you want to use as input.
- Click on the "Output Field" button. Before selecting an output field, you need to run the request to get an example response. Once you have an example response, a drawer will open displaying the "Response Payload" as a JSON Tree. Click on the node representing the field you want to use as output for the assessment.
- Adjust Mission Duration: In the Missions tab, change the
Mission Durationto control the length of the multi-turn interactions.
Example
For example, if your mission is to book a flight from San Francisco to New York, your mission description could be:
"Your mission is to book a flight for two adults from San Francisco to New York. The departure date should be December 20th, and the return date should be December 25th."
The following could be a possible dialogue:
- User: Book a flight from San Francisco to New York for two adults on December 20th, returning on December 25th.
- AI: Sure, I can help with that. What are your preferred airlines?
- User: I don't have a preference. Just find the cheapest option.
- AI: Okay, give me a moment to search for the best deals.
- AI: I found a flight on United Airlines for $450 per person. Would you like to proceed with booking?
- User: Yes, please.
- AI: Great! Can I have the names of the passengers as they appear on their IDs?
- User: John Doe and Jane Doe.
- AI: Thank you. Your flight is now confirmed. You'll receive a confirmation email shortly.
In this example, the LLM would evaluate whether the conversation led to a successful flight booking, considering the mission description and the conversation flow.
Restarting and Deleting
Similar to "Test Runs," you can restart a "Test Mission" using the /runs/invoke API endpoint or the UI's restart button. Deletion is done through the /runs/<run_id> endpoint or the UI's delete button.
Additional Information
- Each mission's conversation history and the final LLM assessment are stored in Firestore, allowing for detailed analysis.
- Consider the ethical implications of multi-turn interactions when crafting your mission descriptions and LLM prompts.
- Experiment with different
Mission Durationsto find a balance between comprehensive evaluation and resource efficiency.
