Test Run Template
The "Test Run" template in Litmus is designed for executing a set of independent test cases against your AI model, primarily focusing on single-turn interactions where you provide an input and expect a specific output. Each test case is treated as an isolated unit, and the results are evaluated individually.
Structure
A "Test Run" template in Litmus consists of the following key components:
- Template ID: A unique identifier for your template.
- Template Data: An array of test cases, each containing:
- Query: The input to your AI model.
- Response: The expected output or "golden answer" from your AI model.
- Filter (optional): Comma-separated keywords or categories to organize and filter test cases.
- Source (optional): A source identifier for the test case.
- Block (optional): A boolean (true/false) indicating whether this test case should be excluded from the run.
- Category (optional): A category or label for the test case.
- Request Payload: A JSON object defining the structure of the request sent to the AI model. It includes placeholders for dynamic values from your test cases, typically using curly braces notation (e.g.,
{query}). - Pre-Request and Post-Request (optional): JSON objects defining optional requests to be executed before and after the main test request, respectively. These are useful for setting up or cleaning up your testing environment.
- LLM Evaluation Prompt (optional): A prompt guiding the LLM in assessing the similarity between the actual responses and the golden responses. This allows for a more nuanced evaluation beyond simple equality checks.
- Input and Output Field Selection: Specifies the exact fields within the request and response payloads to use as input and output for the test cases and LLM assessment.
- Evaluation Types (optional): A dictionary specifying the evaluation methods to use for assessing the LLM responses. This can include:
- Custom LLM Evaluation: Enabled by setting
"llm_assessment": True. Uses the "LLM Evaluation Prompt" to guide the assessment. - Ragas Evaluation: Enabled by setting
"ragas": True. Applies the default set of Ragas metrics. - DeepEval Evaluation: Enabled by providing a list of desired DeepEval metrics within a
"deepeval"list (e.g.,"deepeval": ["answer_relevancy", "faithfulness"]).
- Custom LLM Evaluation: Enabled by setting
Purpose
The primary purpose of a "Test Run" template is to:
- Automate testing of various inputs: Efficiently run numerous test cases against your AI model without manual intervention.
- Verify expected behavior: Ensure your model responds as intended for a range of input queries.
- Identify inconsistencies and regressions: Detect deviations from the expected outputs, highlighting potential issues or regressions in your model.
- Facilitate model improvement: Use the results to refine your model's training data or adjust its parameters.
- Employ multiple LLM evaluation methods: Apply custom prompts, Ragas metrics, and DeepEval evaluations to gain comprehensive insights into your model's performance.
Scenarios
Good Use Cases
- Unit testing individual model functionalities: Verify the accuracy and consistency of specific model capabilities, such as question answering, text summarization, or translation.
- Regression testing after model updates: Ensure that changes to your model haven't introduced unintended consequences or broken existing functionalities.
- Benchmarking model performance against different datasets: Compare your model's performance on various test sets to identify strengths and weaknesses.
Bad Use Cases
- Multi-turn conversations or dialogues: "Test Run" templates are not suitable for testing conversational flows as each test case is independent and lacks context from previous turns. Use "Test Missions" for this purpose.
- Testing model behavior that requires state or context: If your model's output depends on previous interactions or user-specific information, "Test Run" templates might not be appropriate.
Starting a Test Run
CLI
- Get your
RUN_IDandTEMPLATE_ID. - Run the following
litmusCLI command:bashlitmus start $TEMPLATE_ID $RUN_ID
API (Simple)
- Construct a JSON payload with the following information:json
{ "run_id": "your-unique-run-id", "template_id": "your-template-id" } - Send a POST request to the
/runs/submit_simpleendpoint of the Litmus API.
API (Advanced)
- Construct a JSON payload with the following information:json
{ "run_id": "your-unique-run-id", "template_id": "your-template-id", "pre_request": { ... }, // Optional "post_request": { ... }, // Optional "test_request": { ... }, "evaluation_types": { // Optional - specify desired evaluation methods "llm_assessment": True, "ragas": True, "deepeval": ["answer_relevancy", "faithfulness"] } } - Send a POST request to the
/runs/submitendpoint of the Litmus API.
UI
- Navigate to the "Start New Run" page.
- Select your "Test Run" template from the dropdown.
- Enter your
RUN_ID. - Review and modify the request payload if needed.
- (Optional) Configure the evaluation types you want to use.
- Submit the run.
Configuration
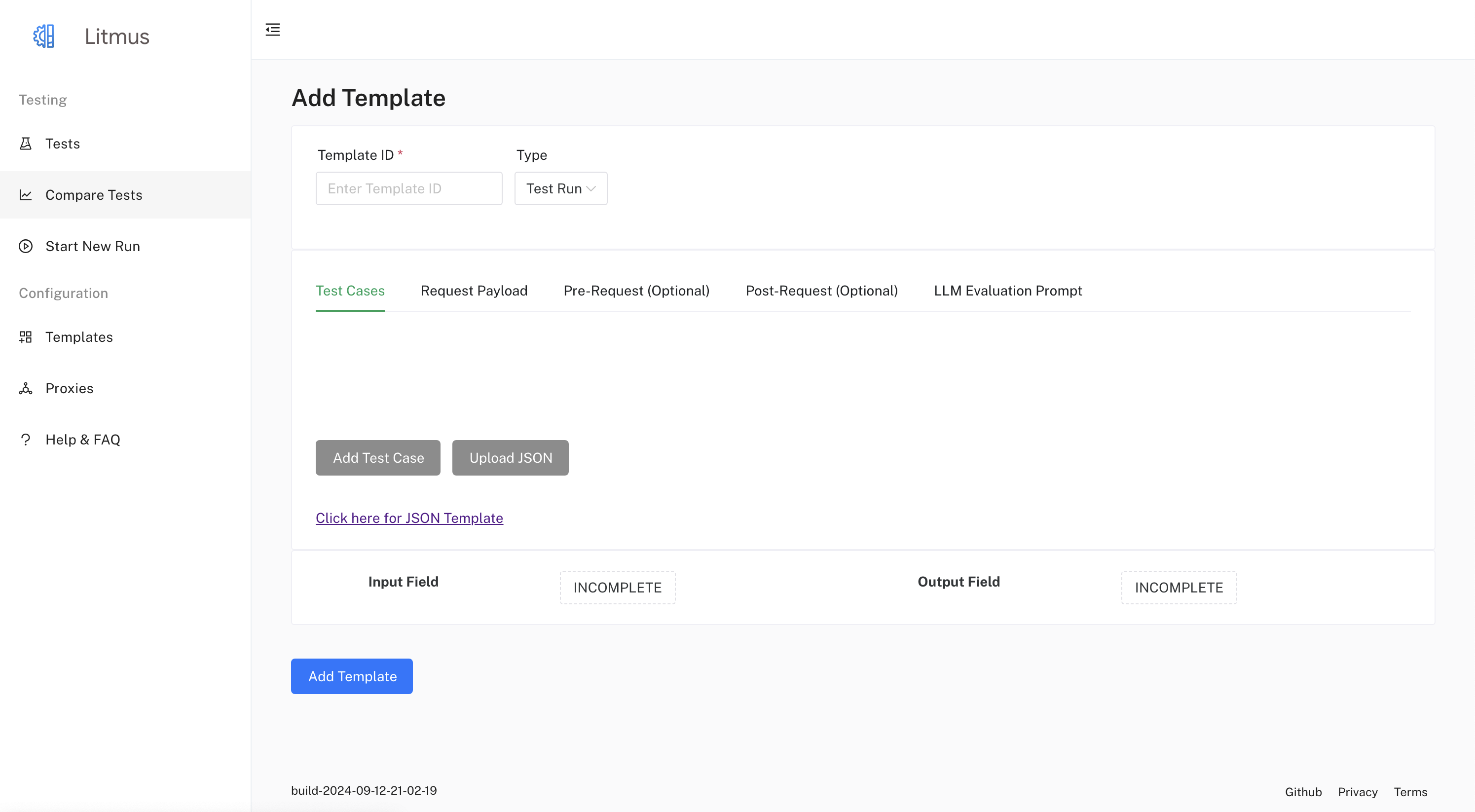
You can configure various aspects of a "Test Run" template in the UI, including:
- Modifying the Template Data: In the Test Cases tab, define or update test cases by adding or removing data items. Each test case item requires a query and an expected response. You can optionally provide additional data like Filter, Source, Block, and Category for each test case item.
- Modifying the Request Payload: In the Request Payload tab, modify the
Request Payloadto match your API requirements by using the built-in JSON editor. Use placeholders (e.g.,{query}) for dynamic values from your test cases or missions. - Defining or updating the Pre-Request and Post-Request: Navigate to the Pre-Request and Post-Request tabs and use the built-in JSON editor to define or update the pre-request and post-request payloads.
- Crafting the LLM Evaluation Prompt: In the LLM Evaluation Prompt tab, enter your prompt in the text area. This prompt will be used if you enable Custom LLM Evaluation in the Evaluation Types.
- Selecting the appropriate Input Field and Output Field:
- Click on the "Input Field" button. A drawer will open displaying the "Request Payload" as a JSON Tree. Click on the node representing the field you want to use as input.
- Click on the "Output Field" button. Before selecting an output field, you need to run the request to get an example response. Once you have an example response, a drawer will open displaying the "Response Payload" as a JSON Tree. Click on the node representing the field you want to use as output for the assessment.
- Selecting Evaluation Types:
- In the "LLM Evaluation Prompt" tab, you can choose which evaluation methods you want to apply.
- You can select any combination of Custom LLM Evaluation, Ragas, and DeepEval.
- For DeepEval, you can choose specific metrics from the available list.
Example
Let's say you're testing a language translation model. A test case might involve a query in English ("Hello, world!") and its expected translation in Spanish ("¡Hola, mundo!"). You'd define the Request Payload to include the English query as {query}, and the model's response would be compared to the expected Spanish translation. You can then choose to evaluate the response using any of the available LLM evaluation methods or a combination of them.
Restarting and Deleting
- Restart: You can restart a "Test Run" by sending a POST request to the
/runs/invokeendpoint with theRUN_IDandTEMPLATE_IDor by using the UI's restart button. - Delete: Delete a "Test Run" by sending a DELETE request to the
/runs/<run_id>endpoint or by using the UI's delete button.
Additional Information
- The results of each test case, including the LLM assessment, Ragas evaluation, and DeepEval results (if selected), are stored in Firestore.
- You can filter and analyze test run results using the UI or by querying the Firestore database directly.
- Consider organizing your test cases using the optional
FilterandCategoryfields for better management and analysis.
