SPEAKER APP¶
The Speaker app is virtual Bluetooth speaker (A2DP sink). The app runs as a command-line executable, but also offers an optional simple web-browser-based user interface.
General Usage¶
You can invoke the app either as bumble-speaker when installed as command
from pip, or python3 apps/speaker/speaker.py when running from a source
distribution.
Usage: speaker.py [OPTIONS] TRANSPORT
Run the speaker.
Options:
--codec [sbc|aac] [default: aac]
--discover Discover remote endpoints once connected
--output NAME Send audio to this named output (may be used more
than once for multiple outputs)
--ui-port HTTP_PORT HTTP port for the UI server [default: 7654]
--connect ADDRESS_OR_NAME Address or name to connect to
--device-config FILENAME Device configuration file
--help Show this message and exit.
Connection¶
By default, the virtual speaker will wait for another device (like a phone or
computer) to connect to it (and possibly pair). Alternatively, the speaker can
be told to initiate a connection to a remote device, using the --connect
option.
Outputs¶
The speaker can have one or more outputs. By default, the only output is a text
display on the console, as well as a browser-based user interface if connected.
In addition, a file output can be used, in which case the received audio data is
saved to a specified file.
Finally, if the host computer on which your are running the application has ffplay
as an available command line executable, the @ffplay output can be selected, in
which case the received audio will be played on the computer's builtin speakers via
a pipe to ffplay. (see the ffplay documentation
for details)
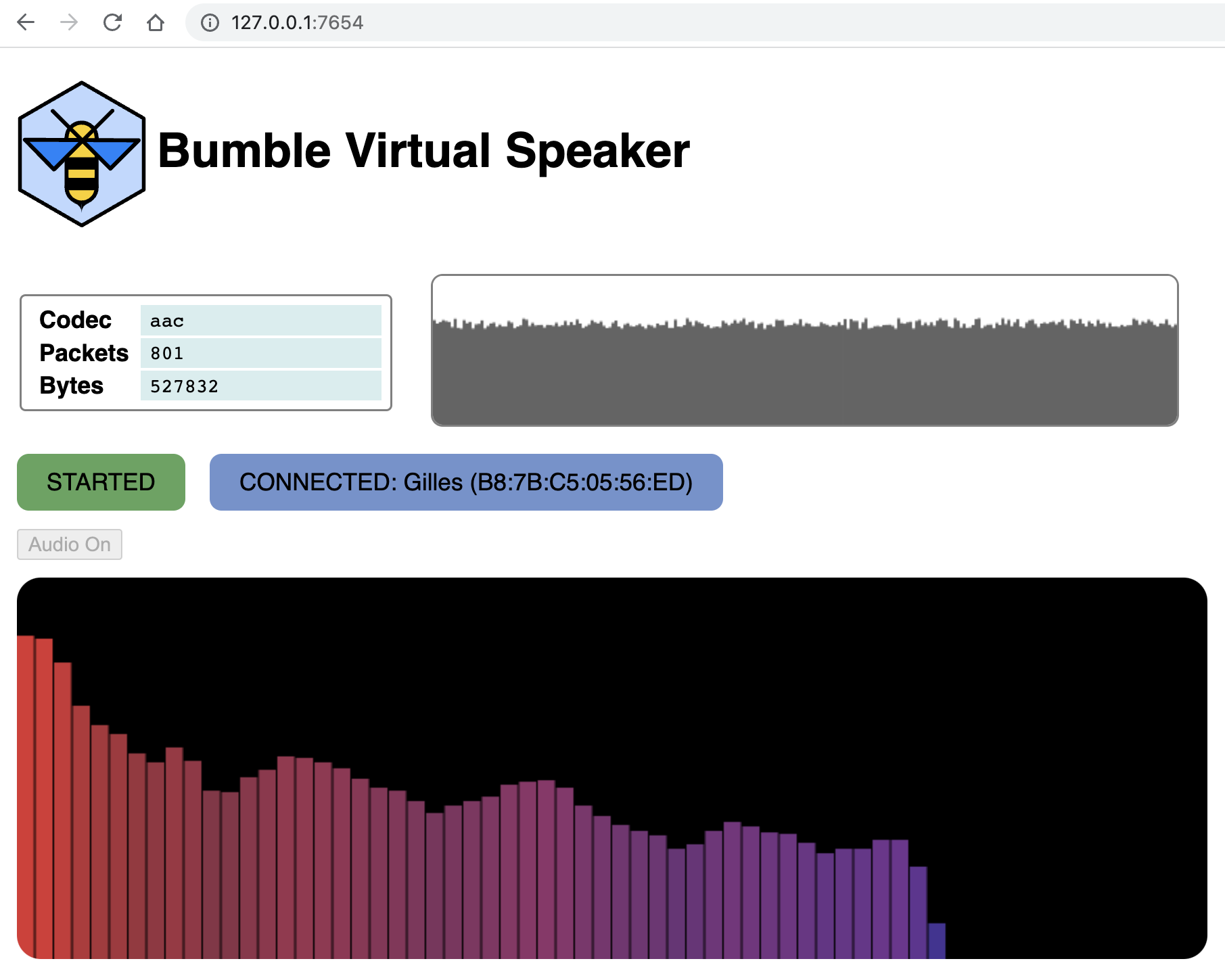
Web User Interface¶
When the speaker app starts, it prints out on the console the local URL at which you may point a browser (Chrome recommended for full functionality). The console line specifying the local UI URL will look like:
UI HTTP server at http://127.0.0.1:7654
By default, the web UI will show the status of the connection, as well as a realtime
graph of the received audio bandwidth.
In order to also hear the received audio, you need to click the Audio on button
(this is due to the fact that most browsers will require some user interface with the
page before granting access to the audio output APIs).
Examples¶
In the following examples, we use a single USB Bluetooth controllers usb:0. Other
transports can be used of course.
Start the speaker and wait for a connection
$ bumble-speaker usb:0
Start the speaker and save the AAC audio to a file named audio.aac.
$ bumble-speaker --output audio.aac usb:0
Start the speaker and save the SBC audio to a file named audio.sbc.
$ bumble-speaker --codec sbc --output audio.sbc usb:0
Start the speaker and connect it to a phone at address B8:7B:C5:05:57:ED.
$ bumble-speaker --connect B8:7B:C5:05:57:ED usb:0