Tree Topology Types
Overview
The tree topology is a hierarchical topology with a root node and children nodes. The radix of a node defines the number of children nodes for the given node. The nodes represent the router nodes and endpoint nodes of a network. A tree topology has endpoints connected to the root router and leaf routers. It is called a tree topology because the router nodes form a tree data structure.
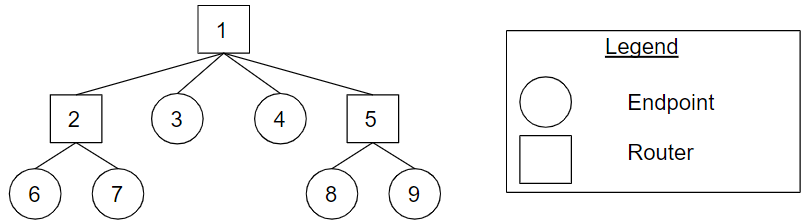
Figure Tree_Topology_Example. A tree topology example.
Figure Tree_Topology_Example shows an example of a tree topology. In the figure, there are nine nodes: three router nodes and six endpoint nodes. Router 1 is a root router, and routers 2 and 5 are leaf routers. Router 1 has a radix of four, and routers 2 and 5 have a radix of two. Routers 2 and 5 are child routers of router 1. Endpoints 3 and 4 are child endpoints of router 1. Endpoints 6 and 7, and endpoints 8 and 9 are child endpoints of router 2 and router 5 respectively.
Unidirectional Types
A unidirectional tree is a tree topology where the communication flow is unidirectional, thus all channels in the tree are unidirectional. There are two unidirectional tree types: aggregation tree and distribution tree.
Aggregation Tree
In the aggregation tree, the communication flow is from the leaf routers of the tree to the root router of the tree. The endpoints connected to the root router receive from the network, and the endpoints connected to the leaf routers send to the network.
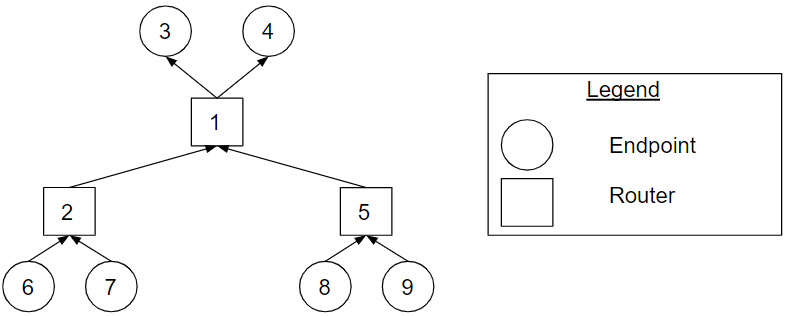
Figure Aggregation_Tree_Topology_Example. The aggregation tree topology representation of the tree in Figure Tree_Topology_Example.
Figure Aggregation_Tree_Topology_Example shows the aggregation tree topology representation of the tree in Figure Tree_Topology_Example. Endpoints 6, 7, 8 and 9 send to the network, and endpoints 3 and 4 receive from the network.
Distribution Tree
In the distribution tree, the communication flow is from the root router of the tree to the leaf routers of the tree. The endpoints connected to the root router send to the network, and the endpoints connected to the leaf routers receive from the network.
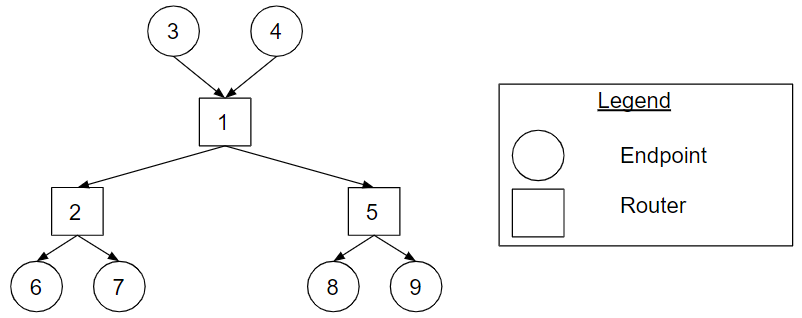
Figure Distribution_Tree_Topology_Example. The distribution tree topology representation of the tree in Figure Tree_Topology_Example.
Figure Distribution_Tree_Topology_Example shows the distribution tree topology representation of the tree in Figure Tree_Topology_Example. Endpoints 3 and 4 send to the network, and endpoints 6, 7, 8 and 9 receive from the network.
Bidirectional Type
A bidirectional tree is a tree topology where the communication flow is bidirectional. The communication flows: from the root router of the tree to the leaf routers of the tree and from the leaf routers of the tree to the root router of the tree. By definition, a bidirectional tree requires: 1) at least one endpoint connected to the root router that sends to the network, 2) at least one endpoint connected to the root router that receives from the network, 3) at least one endpoint connected to the leaf routers that sends to the network, and 4) at least one endpoint connected to the leaf routers that receives from the network. In practice, it is common to have all endpoints connected to the root router and leaf routers send to and receive from the network.
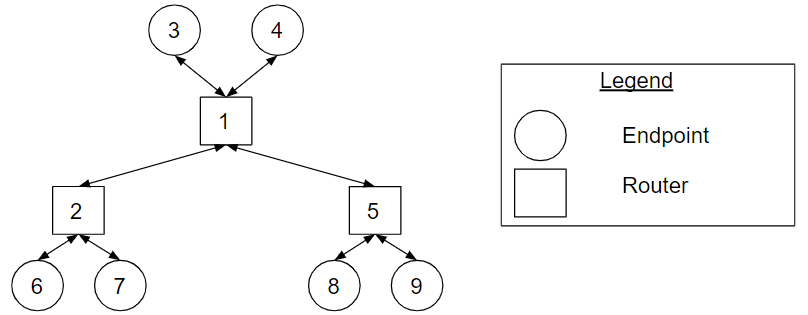
Figure Bidirectional_Tree_Topology_Example. The bidirectional tree topology representation of the tree in Figure Tree_Topology_Example.
Figure Bidirectional_Tree_Topology_Example shows the bidirectional tree topology representation of the tree in Figure Tree_Topology_Example. All endpoints in the tree send to and receive from the network.
Cheat Sheet
- A tree topology has endpoints connected to the root router and leaf routers.
- Unidirectional Trees
- In the aggregation tree, the communication flow is from the leaf routers of the tree to the root router of the tree.
- In the distribution tree, the communication flow is from the root router of the tree to the leaf routers of the tree.
- The communication flow of a bidirectional tree is: from the root router of the tree to the leaf routers of the tree and from the leaf routers of the tree to the root router of the tree.